Configuring Zato for Python Oracle DB connections
If you need to configure Zato for Oracle DB connections and you want to ensure the highest performance possible, this is the post which goes through the process step-by-step. Read on for details.
Overview
Note that Zato 3.1+ is required. The tasks involved are:
- Installing Zato
- Installing an Oracle client
- Installing cx_Oracle
- Greenifying the Oracle client
- Starting servers
- Creating database connection definitions
- Confirming the installation
Installing Zato
Choose your preferred operating system and follow the general installation instructions - Oracle DB connections will work the same no matter the system Zato runs on
Create a Zato environment with as many servers as required. Again, there are no Oracle-specific steps at this point yet.
Installing an Oracle client
Download an Oracle client and install it on all the systems with Zato servers
Add the client's installation path to LD_LIBRARY_PATH. For instance, if the client is installed to /opt/zato/instantclient_19_3, add the following to
~/.bashrc:export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/zato/instantclient_19_3
Installing cx_Oracle
cx_Oracle is a Python driver for Oracle DB, it can be installed using pip, as user zato, on each Linux instance that Zato servers use:
Greenifying the Oracle client
This step is crucial for achieving the highest performance of SQL queries
For each Zato server installed, open its server.conf file and find stanza
[greenify]If there is no such stanza in server.conf, create it yourself
Modify the stanza to greenify the
libclntsh.solibrary - this is a library that the Oracle client ships with. For instance, if the client's installation path is /opt/zato/instantclient_19_3, the full path to the library is /opt/zato/instantclient_19_3/libclntsh.soThe stanza should read as below, assuming the installation path as above:
- Note that entries in this stanza are followed by
=True, which is a signal to Zato that a particular library should be processed
Starting servers
- Start Zato servers
For each, make sure that an entry such as below is saved in server logs
Creating database connection definitions
- Go to web-admin and create a new Oracle DB connection via Connections -> Outgoing -> SQL, as below:
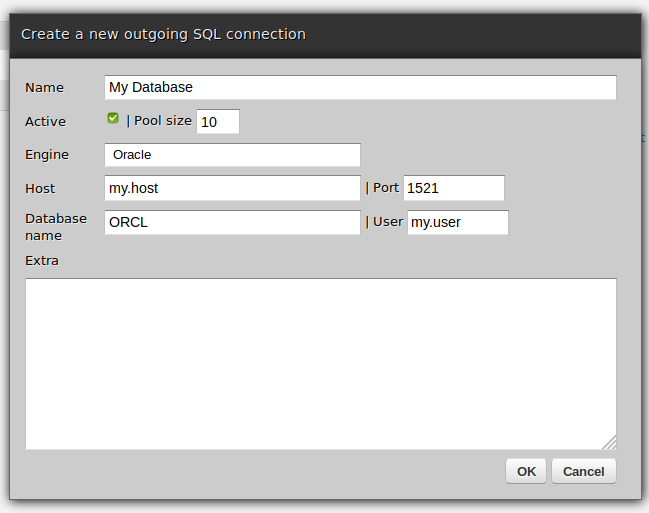
Update the newly created connection's password by clicking
Change passwordClick
Pingto confirm the connectivity to the remote serverThis concludes the process, the connection is ready for use in Zato services now
