In this article, we will cover the details of how Zato SQL connection pools can be configured to take advantage of features and options specific to a particular driver or to the SQLAlchemy library.
First, let's review the basic Zato Dashboard form that creates a new SQL connection pool.
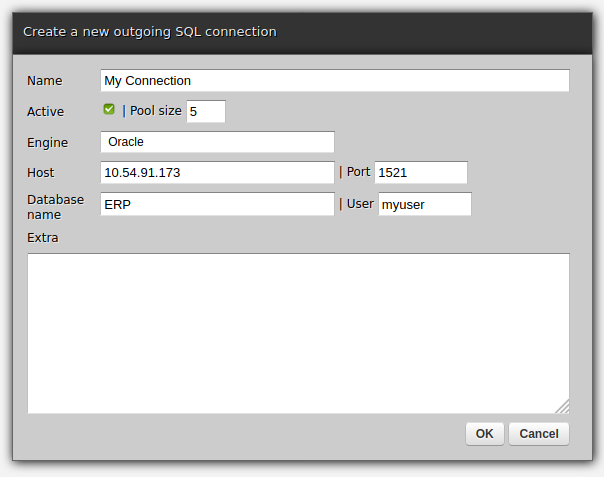
Above, we find options that are common to all the supported databases:
The basic form covers the most often required, common options but there is more to it and that comes in two flavors:
As to how to declare them:
Options from the first group are specified using a query string appended to the database's name, e.g. mydb?option=value&another_option=another_value.
Options from the second group go to the Extra field in the form.
We will cover both of them using a few practical examples.
When connecting to MySQL, there may arise a need to be explicit about the character set to use when issuing queries. This is a driver-level setting so it is configured by adding a query string to the database's name, such as mydb?charset=utf8.
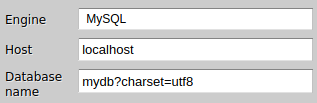
At this point, you may wonder about how to learn which options can be used by which driver and what can go to the extra field?
The driver-specific options will be in that particular library's documentation - each one will have a class called Connection whose __init__ method will contain all such arguments. This is what the query string is built from.
As for the extra field - it accepts all the keyword arguments that SQLAlchemy's sqlalchemy.create_engine function accepts, e.g. in addition to echo, it may be max_overflow, isolation_level and others.
And that sums up this quick how-to - now, you can configure more advanced SQL options that are specific either to each driver or to SQLAlchemy as such.