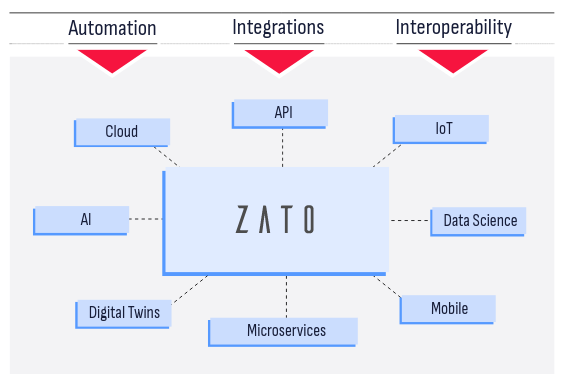
Zato is an open-source, Python-based integration platform that lets you build and deliver enterprise solutions with ease, from online APIs, business processes, data science, AI, ML, IoT, mainframe and cloud migrations to automation, digital transformation, knowledge graphs and state-of-the-art technologies, combining ease of use with safety and security