Download and install Docker Desktop for your operating system
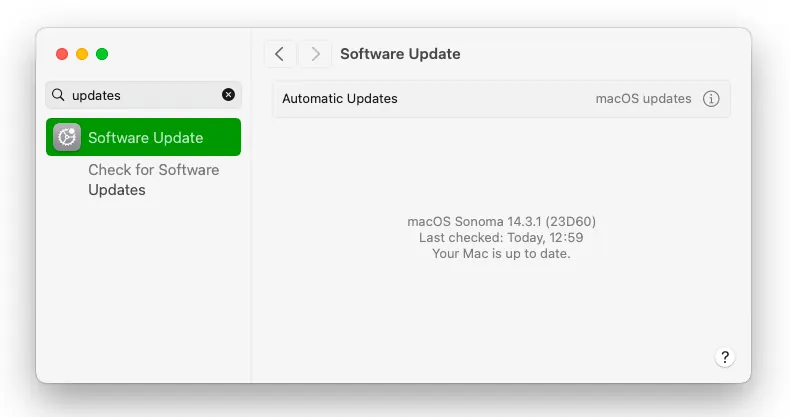
On Mac, if you have Apple silicon, make sure to install all the updates for your system because newest Docker versions may be incompatible with upatched macOS systems
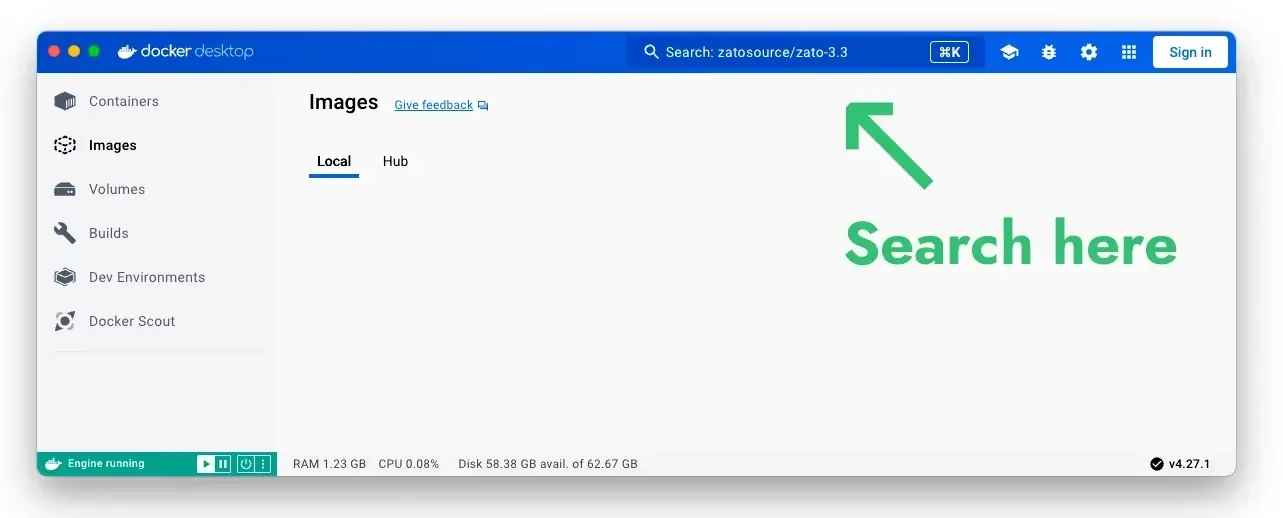
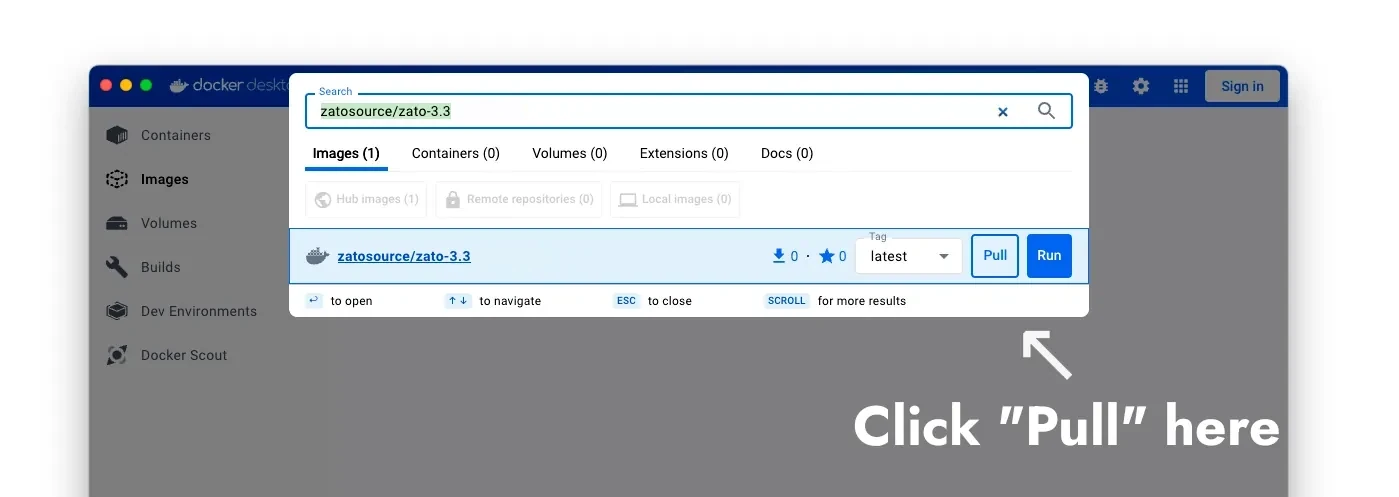
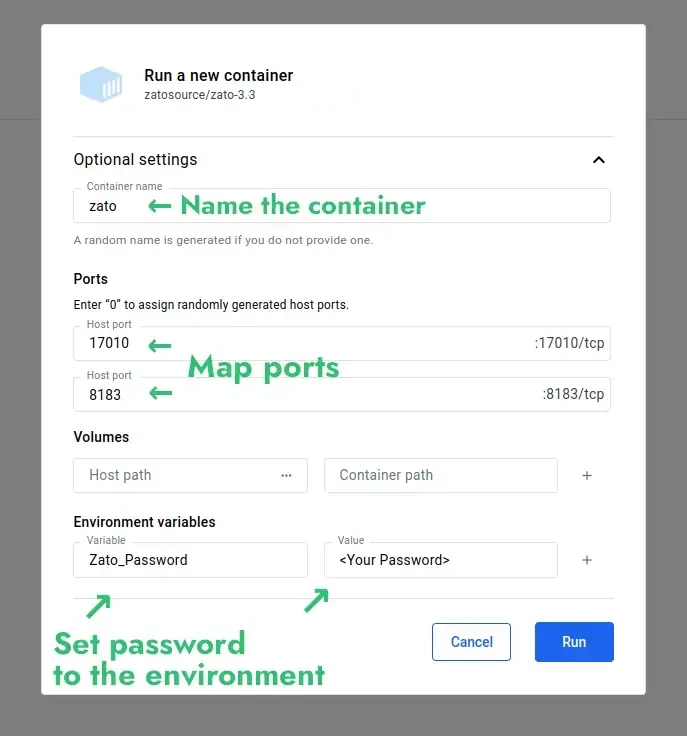
sudo docker run --pull=always -it --rm -p 22022:22 -p 8183:8183 -p 11223:11223 -p 17010:17010 \
--name zato-4.1 -e Zato_Log_Env_Details=True \
zatosource/zato-4.1
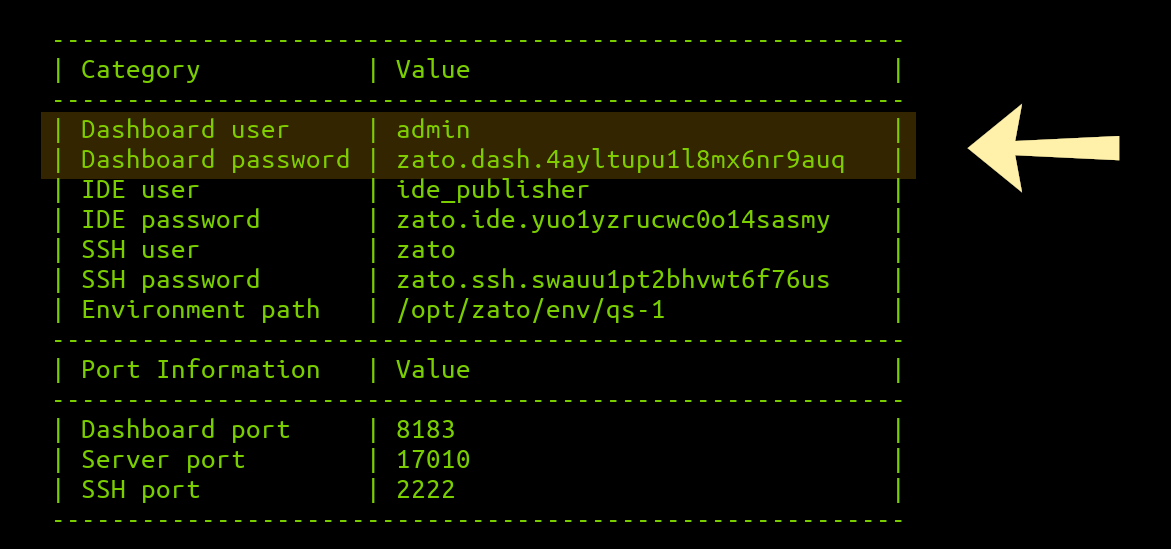
---------------------------------------------------------
| Category | Value |
---------------------------------------------------------
| Dashboard user | admin |
| Dashboard password | ... |
| IDE user | ide_publisher |
| IDE password | ... |
| SSH user | zato |
| SSH password | ... |
| Environment path | /opt/zato/env/qs-1 |
---------------------------------------------------------
| Port Information | Value |
---------------------------------------------------------
| Dashboard port | 8183 |
| Server port | 17010 |
| SSH port | 2222 |
---------------------------------------------------------
Docker Compose provides a declarative way to define and run your Zato environment with persistent configuration and services.
Create a docker-compose.yml file in your project directory:
version: '3.8'
services:
zato:
image: ghcr.io/zatosource/zato-4.1:latest
container_name: zato-quickstart
ports:
- "8183:8183"
- "17010:17010"
- "11223:11223"
- "22022:22"
environment:
- Zato_Password=mypassword
- Zato_Log_Env_Details=True
restart: unless-stopped
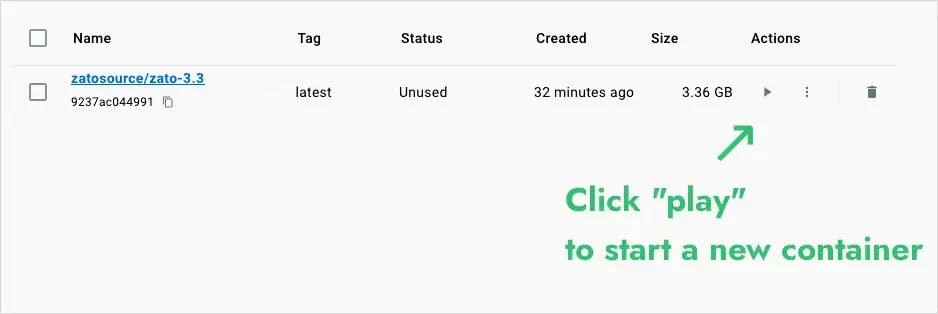
Start the container:
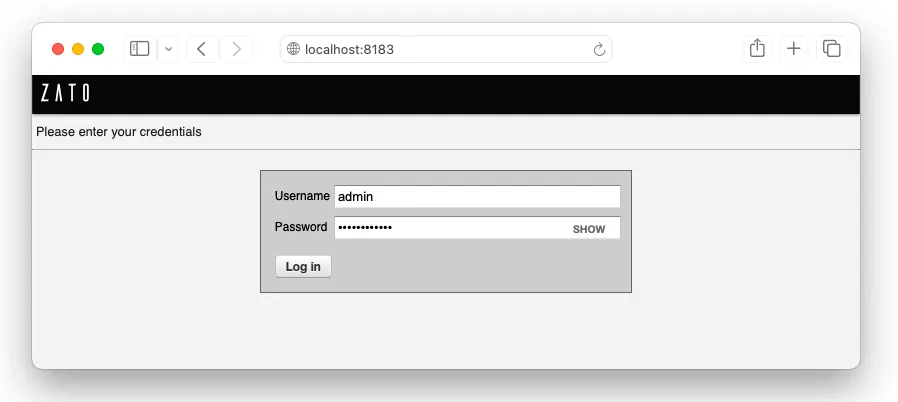
Access your Dashboard at http://localhost:8183: * Username: admin * Password: mypassword
For production environments, mount your project directories to persist configuration and services:
version: '3.8'
services:
zato:
image: ghcr.io/zatosource/zato-4.1:latest
container_name: zato-production
ports:
- "8183:8183"
- "17010:17010"
- "11223:11223"
- "22022:22"
environment:
- Zato_Dashboard_Password=${ZATO_DASHBOARD_PASSWORD}
- Zato_IDE_Password=${ZATO_IDE_PASSWORD}
- Zato_SSH_Password=${ZATO_SSH_PASSWORD}
- Zato_Log_Env_Details=True
- Zato_Env_Name=Production
volumes:
- ./myproject:/opt/hot-deploy/myproject:ro
- ./myproject/config/enmasse/enmasse.yaml:/opt/hot-deploy/enmasse/enmasse.yaml:ro
- ./myproject/config/auto-generated/env.ini:/opt/hot-deploy/enmasse/env.ini:ro
- ./myproject/config/python-reqs/requirements.txt:/opt/hot-deploy/python-reqs/requirements.txt:ro
restart: unless-stopped
Create a .env file in the same directory to store passwords:
ZATO_DASHBOARD_PASSWORD=your_secure_password
ZATO_IDE_PASSWORD=your_ide_password
ZATO_SSH_PASSWORD=your_ssh_password
Start the environment:
Override default ports to avoid conflicts:
version: '3.8'
services:
zato:
image: ghcr.io/zatosource/zato-4.1:latest
container_name: zato-custom-ports
ports:
- "9000:9000"
- "18000:18000"
- "12000:12000"
- "23000:22"
environment:
- Zato_Port_Dashboard=9000
- Zato_Port_Server=18000
- Zato_Port_Load_Balancer=12000
- Zato_Password=mypassword
- Zato_Log_Env_Details=True
restart: unless-stopped
Access monitoring dashboards alongside Zato:
version: '3.8'
services:
zato:
image: ghcr.io/zatosource/zato-4.1:latest
container_name: zato-monitored
ports:
- "8183:8183"
- "17010:17010"
- "11223:11223"
- "35672:15672"
- "33033:3000"
- "39090:9090"
environment:
- Zato_Password=mypassword
- Zato_Prometheus_Password=prom123
- Zato_Log_Env_Details=True
restart: unless-stopped
View logs:
Stop the environment:
Restart the environment:
Pull latest image and recreate:
For a complete list of available environment variables, see the Environment Variables Reference.